SKC Films Library |
| SKC Films Library >> Science >> Geology >> Dynamic and Structural Geology |
| Four Ways to "Make" a Mountain Mountainous regions are created by movements of the earth's crust. These movements occur very slowly, but on a large scale. Different parts of the earth's crust react in different ways to these movements, and form four basic types of mountains. Volcanism
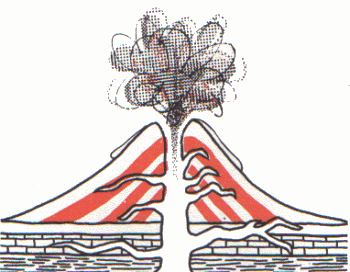
Outpouring lava and ash build a cone-shaped peak. The Hawaiian Islands are volcanic mountains that have "grown" out of the sea. The Cascades of the Pacific Northwest are also volcanic in origin. Folding
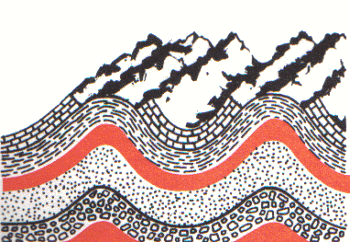
"Fold mountains" are created when two crustal plates meet "head-on" and push against each other. Ranges created in this way often resemble huge washboards. The Himalaya lie along the line where the Indian Subcontinent meets the Eurasian landmass, the Appalachians of the eastern United States were created by the pressure of the Atlantic Ocean plate "slamming" into the North American plate, and the Alps "mark" the boundary between the European and African plates. Faulting
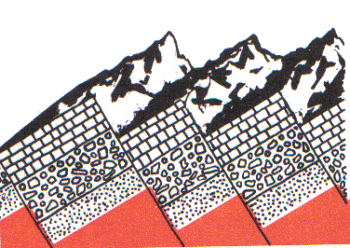
Movement along breaks or faults between huge blocks of rock makes mountains that may be quite high and steep. The Sierra Nevada in California were formed by movements of the infamous San Andreas fault line. Doming
The core of a dome mountain was once magma, which pushed up the rocks above it into a sort of blister. The Black Hills of South Dakota and the mountains of Great Britain's Lake District were formed in this manner. SEE ALSO |
| SKC Films Library
>> Science >> Geology >> Dynamic and Structural Geology This page was last updated on 12/16/2017. |