| Democratic
Republic of São Tomé and Principe Republica Democratica de São Tomé e
Principe
Origin of Name
São Tomé was named after Saint Thomas
the Apostle by the Portuguese who discovered the
island on December 21, 1470 (or 1471), the
saint's feast day; Principe is a shortening of
the original Portuguese name of "Ilha do
Principe" (Isle of the Prince), referring to
the Prince of Portugal to whom duties on the
island's sugar crop were paid
Location about 150
miles off the western coast of Africa
Nearest Mainland Neighbor Gabon
Total Area 372
sq mi (964 sq km)
Highest Point Pico de São
Tomé; 6,640 ft (2,024 m)
Lowest Point sea level
Natural Resources fish,
hydropower
Nationality
São Toméan
Population (July 2015 est) 194,006
Largest City São Tomé
Ethnic Groups mestico,
angolares (descendants of Angolan slaves), forros
(descendants of freed slaves), servicais
(contract laborers from Angola, Mozambique, and
Cabo Verde), tongas (children of servicais born
on the islands), Europeans (primarily
Portuguese), Asians (mostly Chinese)
Languages Portuguese (official),
Forro, Cabo Verdian, French, Angolar, English,
Lunguie
Religions Catholic, none,
Adventist, Assembly of God, New Apostolic, Mana,
Universal Kingdom of God, Jehovah's Witnesses
Capital São
Tomé
Form of Government
semi-presidential republic
Present Constitution Adopted
November 5, 1975
Chief of State President Evaristo
Carvalho (since August 7, 2016)
Head of Government Prime Minister
Patrice Emery Trovoada (since November 29, 2014)
Cabinet Council of Ministers; proposed
by the Prime Minister, appointed by the President
Legislature unicameral National Assembly
(Assembleia Nacional)
Judiciary Supreme Court, Constitutional
Court
Local Administration 2 provinces
Currency Dobra
(STD)
Per Capita Income $3,200
Industries light
construction, textiles, soap, beer, fish
processing, timber
Agricultural Products cocoa,
coconuts, palm kernels, copra, cinnamon, pepper,
coffee, bananas, papayas, beans; poultry; fish
Export Commodities cocoa, copra,
coffee, palm oil
Import Commodities machinery and
electrical equipment, food products, petroleum
products
 Independence from Portugal
Achieved July 12, 1975 Independence from Portugal
Achieved July 12, 1975
National Holiday Independence
Day; July 12
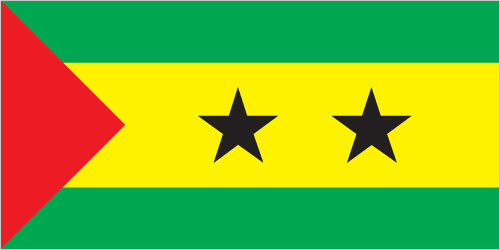
Flag three horizontal
bands of green (top), yellow (double width), and
green with two black five-pointed stars placed
side by side in the center of the yellow band and
a red isosceles triangle based on the hoist side;
green stands for the country's rich vegetation,
red recalls the struggle for independence, and
yellow represents cocoa, one of the country's
main agricultural products; the two stars
symbolize the two main islands

Gabon
Questions or comments about
this page?
|



