| Gabonese Republic République Gabonaise
Origin of Name Gabon's first European
visitors were Portuguese traders who arrived in the 15th
century and subsequent Portuguese references refered to
it as Gabon after the Portuguese word "gabao,"
a coat with sleeves and hood resembling the shape of the
Como River estuary, where they first explored.
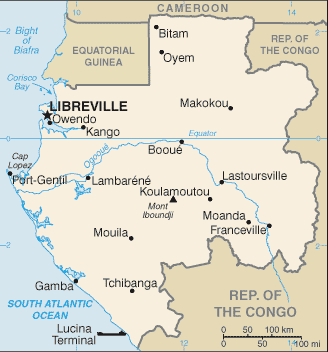
Location west central
Africa
Bordered By Equatorial
Guinea, Cameroon, Republic of the Congo
Area 103,347 sq mi
(267,667 sq km)
Coastline 500 mil (800 km)
Highest Point Mont Iboundji; 5,167 ft
(1,575 m)
Lowest Point sea level along the coast
Natural Resources oil, manganese,
uranium, iron, gold
Nationality Gabonese
Population (July 2014 est) 1,672,597
Largest Cities Libreville, Port-Gentil,
Franceville
Ethnic Groups Fang, Myene, Bapounou,
Eshira, Bandjabi, Bakota, Nzebi, Bateke/Obamba
Religions Christian, Muslim
Languages French (official), Fang,
Meyene, Bateke, Bapounous/Eschira, Bandjabi
Capital Libreville
Form of Government republic
Present Constitution Adopted March 15,
1991
Chief of State President Ali Bongo
Ondimba (since October 16, 2009)
Head of Government Prime Minister Emmanuel
Issoze-Ngondet (since September 29, 2016)
Cabinet Council of Ministers
Legislature bicameral
Judiciary Supreme Court, Constitutional Court
Local Administration 9 provinces
Currency Cooperation
Financiere en Afrique Centrale franc
Per Capita Income $18,100
Industries oil products, textiles, food
and beverages
Agriculture cocoa, coffee, palm products
Export Commodities petroleum, wood,
manganese
Import Commodities construction
equipment, machinery, food, automobiles, manufactured
goods
Independence From France
Achieved August 17, 1960
National Holiday Independence Day;
August 17
Flag green represents the
country's forests and natural resources, gold represents
the equator (which transects Gabon) as well as the sun,
blue represents the sea

SEE ALSO
Equatorial
Guinea
Cameroon
Republic
of the Congo
Questions or comments about this
page?
|
 SKC Films Library
SKC Films Library
