SKC Films Library |
| SKC Films Library >> American History >> Canada >> Northwest (General) |
| Hudson's Bay Company Founded in London in 1670 for the purpose of establishing a fur trade in the Hudson Bay region, HNC is now the oldest continuously operating company in America. Official seal of the Hudson's Bay
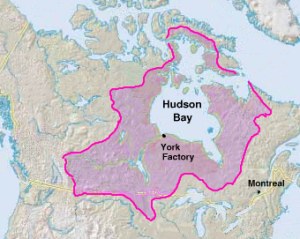
Company. Beginnings A group of English merchants and noblemen founded the Hudson's Bay Company with the help of two French fur traders, Pierre-Esprit Radisson and Medard Chouart, Sieur des Groseilliers. The two traders knew that furs from North America could earn fortunes. In 1668, Groseilliers helped direct a trading expedition to the Hudson Bay region. The expedition was so successful that King Charles II of England gave the Hudson's Bay Company a charter in 1670. The "Charter of the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading into Hudson Bay" granted the company sole trading rights in all lands drained by the streams that flowed into Hudson Bay, and Prince Rupert, the HBC's leader, was named Governor of the vast territory, which came to be known as Rupert's Land. The company had the power to establish laws and impose penalties for violating those laws, to erect forts, to maintain ships of war, and to make peace or war with the natives. Company agents built trading posts and forts along the bay, from which they traded with the Native Americans and exchanged such goods as beads, kettles, and knives for beaver pelts. In England, the pelts were made into expensive felt for garments and hats. The territory controlled by the
Hudson's Bay Company. Trouble with the French Almost from its inception, the company struggled with the French, who also claimed the Hudson Bay region. In 1697, Pierre le Moyne d'Iberville defeated the HBC ships Hudson's Bay, Hampshire, and Dering, and burned Fort Nelson. The Treaty of Ryswick was signed that same year, giving the French control of all settlements along the bay for 17 years. In 1713, the Treaty of Utrecht returned the Hudson Bay region to Britain, but troubles with France continued. Those disputes over trading rights in the Hudson Bay region provided the impetus for the French and Indian War, which was fought from 1756 to 1763. The Treaty of Paris, which officially ended the war, ceded virtually all French possessions in North America to England, and gave the HBC an almost complete monopoly of the fur trade. Competition and Growth During the late 1770's, a group of independent Canadian fur traders organized the North West Company to compete with the Hudson's Bay Company. Because of the growing competition, the HBC sent expeditions far inland to find new sources of furs, including one led by Alexander MacKenzie which crossed the Rockies and reached the Pacific Coast. The company's explorers established a network of trading posts and transport routes, thus opening Canada to settlement all the way to the Pacific. In 1821, the two rival companies combined under the name Hudson's Bay Company, which was completely reorganized under the leadership of Sir George Simpson. The British Parliament granted the new company a 21-year monopoly over fur trade in British North America west of Upper Canada, giving it control over 3 million square miles of land; the monopoly was extended for another 21 years in 1838. Post-Monopoly In 1859 the trade monopoly was abolished and trade in the region was opened to any entrepreneur. The claims of the company to vested interest and property rights, however, remained unsettled until 1870, when Rupert's Land was acquired by the Dominion of Canada in return for an indemnity of approximately $600,000 and a land grant of 7 million acres. The company retained its forts and trading posts, but gave up all monopolistic privileges. Vast portions of the land grant were subsequently sold to settlers, adding several million dollars to the company's coffers. The Company Today By the early 1900's, many of the original Hudson's Bay Company trading posts had evolved into full-scale retail establishments. Between 1910 and 1914 the company built and expanded department stores in Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton and Victoria. Over the subsequent decades the company has shed its fur-trading enterprises in favor of retail department stores, and is today one of the largest department store chains in North America. The official website of the Hudson's Bay Company is www.hbc.com. Official flag of the Hudson's Bay
Company. PRINT SOURCE INTERNET SOURCE SEE ALSO |
| SKC Films Library
>> American History
>> Canada >> Northwest (General) This page was last updated on 10/24/2017. |